9 Mistakes E-commerce Brands Make When Implementing AI Agents
Avoid the common pitfalls of e-commerce AI implementation. Learn how to transition from basic chatbots to revenue-driving "agentic commerce" by focusing on task execution, unified customer journeys, and real-time data integration.
The "AI revolution" in e-commerce has reached a frustrating plateau. Many brands have deployed an AI agent only to find they’ve built expensive FAQ machines that fail to move the needle on revenue or customer lifetime value. While these chatbots were intended to revolutionize customer service, they often lack the depth to solve a real business need.
The reality? AI agents aren't failing; implementations are. Most projects fail quietly, not with a crash, but with a slow fade into irrelevance as customers revert to traditional filters or, worse, competitors. To succeed, brands must move beyond basic tools that simply automate text and transition toward true agentic commerce.
TL;DR
Most e-commerce brands fail by deploying limited chatbots that only answer FAQs instead of driving revenue. To succeed in agentic commerce, your AI agent must move beyond basic automation to solve real business needs. Alhena AI helps brands avoid common pitfalls by providing an agent that acts autonomously to manage complex workflow tasks, like real-time inventory checks, while scaling customer service to personalize the customer experience.
In this new workflow, an AI agent must act autonomously to personalize the customer experience, managing everything from complex styling advice to real-time inventory checks. We’ve identified nine common mistakes brands make and the high-impact strategies to ensure your e-commerce AI strategy actually delivers.
1. The "Smarter Chatbot" Fallacy
Many brands treat an e-commerce AI agent as a slightly more articulate chatbot. This is a fundamental misunderstanding of the technology.
- The Mistake: Deploying agents that can only answer questions rather than execute tasks. If your AI can tell a customer your return policy but can’t help them find a specific outfit for a beach wedding, it’s a cost centre, not a growth engine.
- The Pivot: Adopt an "agentic" mindset. AI agents should be autonomous partners capable of guiding discovery, influencing purchase decisions, and completing complex workflows.
What is the difference between traditional chatbots and an ecommerce AI agent?
While traditional chatbots typically follow rigid, predefined scripts, an AI agent operates autonomously to handle complex requests. Unlike basic automation, a true agent can manage a sophisticated workflow, such as checking real-time inventory or guiding a customer through a complete purchase journey, rather than just answering FAQs.
2. Decoupling AI from Bottom-Line Outcomes
If your primary KPI for AI is "tickets deflected", you are treating your AI like a shield rather than a salesperson.
- The Mistake: Failing to tie AI performance to revenue-centric metrics.
- The Pivot: Measure AI agents as a sales channel. Track Assisted Conversion Rate, AOV Uplift, and Time-to-Purchase. Leadership buys into ROI, not just CSAT.
3. Training on "Dirty" or Fragmented Data
An AI agent is only as sophisticated as the data it consumes.
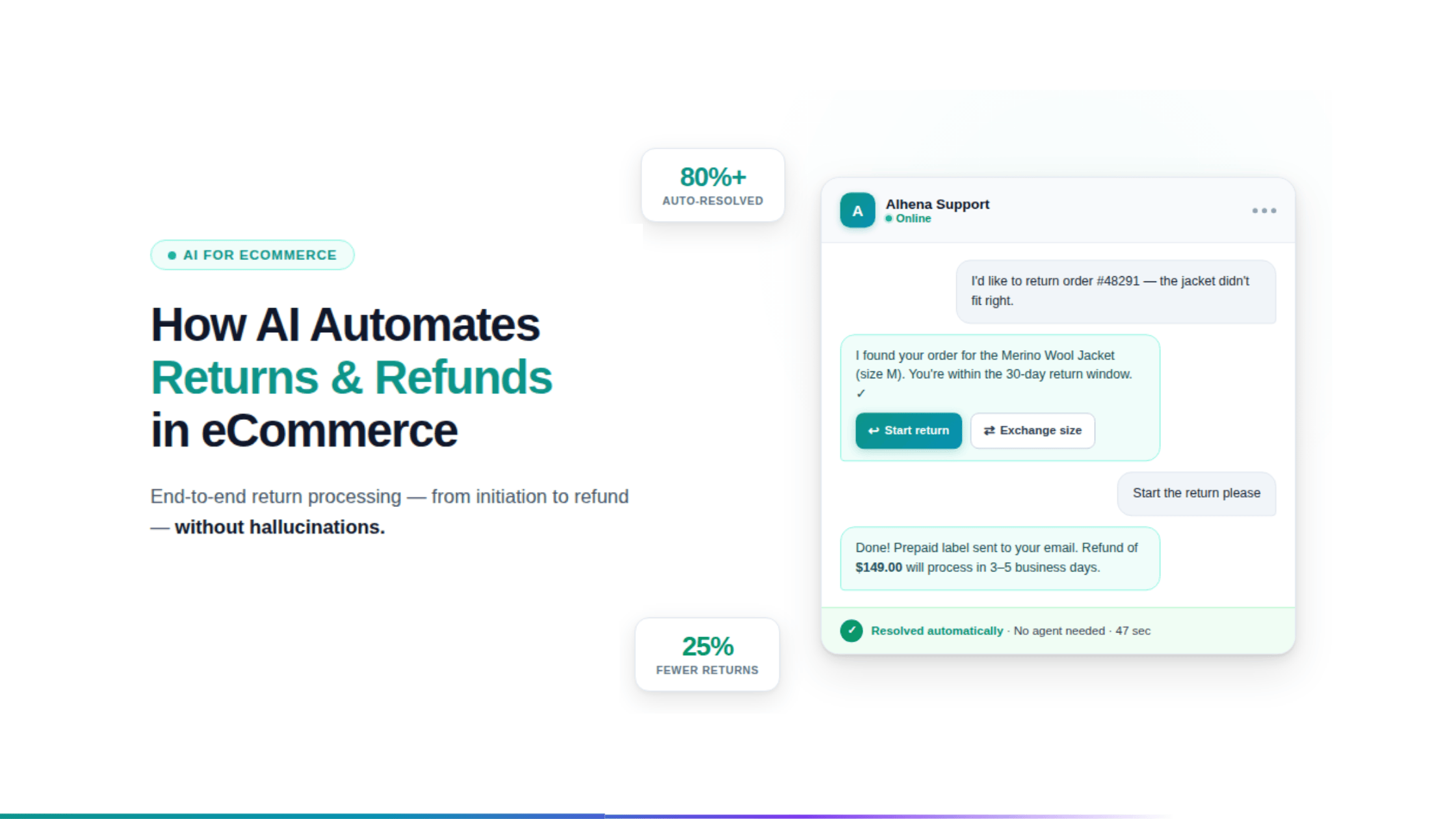
- The Mistake: Feeding the agent outdated PDFs or a messy product catalog. This leads to "hallucinations", where the AI confidently recommends a product that is out of stock or describes features that don't exist.
- The Pivot: Invest in a "Commerce-Ready" Knowledge Base. Ensure your agent has real-time access to your full catalog, current merchandising logic, and active promotional calendars.
4. Ignoring the Nuance of Conversational Search
Shoppers do not talk like database queries. They don't say "Category: Dresses; Color: Black; Price: <100." They say, "I need something chic for a cocktail party that hides my midsection."
- The Mistake: Optimizing AI to function like a set of rigid filters.
- The Pivot: Implement conversational search that understands intent and context. The goal is to handle vague queries and refine results through natural dialogue, mimicking an elite in-store associate.
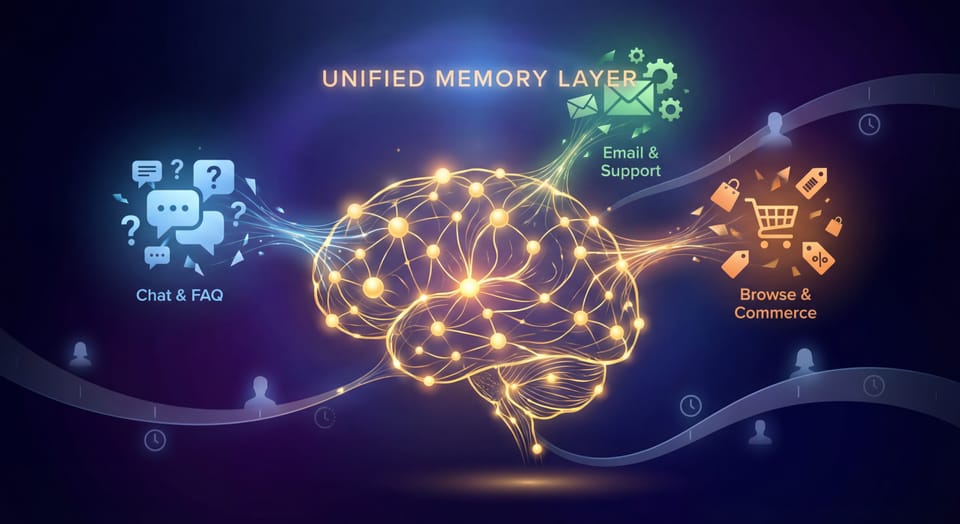
5. Creating a Fragmented Customer Journey
There is nothing more frustrating for a customer than explaining their problem to a "Search Bot" only to have to repeat it to a "Support Bot".
- The Mistake: Using siloed AI tools for different stages of the funnel.
- The Pivot: Deploy a unified AI agent that maintains context from discovery through post-purchase. This creates a frictionless, "gold-standard" CX where the agent remembers the customer’s style preferences when they return for support.
6. The "All-or-Nothing" Automation Trap
In an attempt to cut costs, brands often remove the "human in the loop" too early.
- The Mistake: Forcing AI to handle complex edge cases it isn't trained for, leading to a "loop of doom" for the customer.
- The Pivot: Use a Hybrid Agent Model. AI should handle 80-90% of queries, but the system must allow for a seamless, high-context handoff to a human representative the moment the sentiment shifts or the query becomes too complex.
Are AI agents replacing human agents in e-commerce?
No. AI agents augment human agents by automating repetitive tasks and workflows. This allows human teams to focus on high-value interactions that improve customer experience and long-term loyalty.
7. Diluting the Brand Voice
A generic, robotic AI agent acts as a brand detractor, especially for premium or luxury labels.
- The Mistake: Using "out-of-the-box" personalities that don't reflect your brand’s unique tone or merchandising sales playbooks.
- The Pivot: Fine-tune your AI on your brand’s specific vernacular. Whether you are "playful and Gen Z" or "authoritative and luxury," your AI agent must be an extension of your marketing team.
8. Treating AI as a "Set and Forget" Project
E-commerce is dynamic. Trends shift, catalogs update, and customer language evolves.
- The Mistake: Deploying an agent and never reviewing the transcripts or performance data.
- The Pivot: Commit to continuous optimization. Regularly analyze "unanswered queries" to identify gaps in your knowledge base and tune the AI’s recommendation logic based on conversion data.
What business needs do ecommerce AI agents solve?
AI agents address core business needs like automation, customer service scalability, workflow efficiency, and personalization. They help brands increase revenue while reducing operational costs.
9. Measuring Success Through the Wrong Lens
If you measure a high-performing sales agent only by how fast they get off the phone, you’ve missed the point.
- The Mistake: Evaluating AI agents solely as support tools.
- The Pivot: View AI as a Revenue Multiplier. Look at how the agent influences the "LTV of an AI-assisted customer" versus a "non-assisted customer."
The Blueprint for Success: How Modern Brands Scale
To win in the age of conversational commerce, leading brands follow a simple five-pillar framework:
- Outcome-First Design: Start with the revenue goal, then build the prompt.
- Unified Context: One agent, one journey.
- Deep Commerce Training: Catalog integration is non-negotiable.
- Conversational-First UX: Move beyond buttons and filters.
- The Feedback Loop: Use AI insights to inform your broader marketing strategy.
Redefining Ecommerce with Alhena AI
At Alhena AI, we built our platform specifically to solve these nine points of failure. Unlike generic chatbots, Alhena is an all-in-one ecommerce AI agent designed to bridge the gap between discovery and conversion. By combining deep product knowledge with brand-aligned conversational intelligence, we help brands turn "browsers" into "buyers" through hallucination-free, revenue-driven interactions.
The future of e-commerce isn't just digital; it's agentic.
Are you ready to evolve beyond the chatbot? Schedule a demo session with Alhena AI, and let’s audit your current AI implementation.
FAQs
Can an AI agent actually automate complex commerce tasks?
Yes. Modern agentic systems are designed to automate more than just text responses. They can integrate directly into your commerce backend to execute tasks like processing returns, updating shipping details, or managing multi-step orders without human intervention.
How do AI agents improve the customer experience in e-commerce?
An AI agent enhances the customer experience by providing a highly personalized shopping journey. By understanding natural language and intent, these agents go beyond standard customer service to act as digital concierge, helping shoppers find exactly what they need within a vast e-commerce catalog.
Do AI agents work autonomously or need constant supervision?
Modern AI agents can operate autonomously for most e-commerce use cases, including order tracking, product discovery, and support. Human oversight is only required for edge cases or strategic optimization.
Can AI agents personalize shopping experiences at scale?
Yes. AI agents personalize e-commerce journeys by understanding intent, preferences, and context, delivering tailored recommendations, responses, and next-best actions for every shopper.
How do AI agents fit into agentic commerce?
In agentic commerce, AI agents act as proactive participants in the buying process, searching, recommending, personalizing, and executing actions autonomously to streamline commerce end to end.