9 AI Agent Use Cases Transforming E-commerce in 2026
Explore e-commerce AI agent use cases shaping commerce in 2026, from autonomous shopping to hallucination-free support and revenue growth.
AI agents represent a shift from reactive to proactive, data-driven operations in e-commerce. By unifying data and acting on it in real time, agents offer e-commerce businesses new ways to scale high-quality tailored interactions, optimize processes, and reduce costs.
Today’s leading brands are no longer just "adding AI" to their stores; they are rebuilding their entire customer journey around agentic commerce. These aren't just chatbots that answer questions; they are autonomous digital employees that reason, execute tasks across your tech stack, and drive measurable growth.
TL;DR
In 2026, ecommerce success is defined by Agentic Commerce, moving beyond "chatty" bots to autonomous AI agents that reason and act. While traditional tools struggle with hallucinations, Alhena AI provides a shopping-first, hallucination-free architecture that automates up to 90% of L1 support and proactively drives revenue through personalized discovery and real-time cart recovery.
What is an e-commerce AI agent?
An e-commerce AI agent is an autonomous system designed to understand complex shopper intent, access real-time business data (inventory, ERP, CRM), and execute multi-step actions to resolve customer needs.
Unlike traditional chatbots that rely on scripted "if-then" logic, AI agents use reasoning to achieve a goal, whether that is finding the perfect product, processing a complex exchange, or recovering a high-value abandoned cart.
Here are 9 AI agent use cases defining the future of e-commerce:
1. The Autonomous Shopping Concierge
Agentic commerce marks a fundamental shift in how brands build relationships. Standard search and filters often fail when shoppers don't know the technical terms for what they need. AI shopping concierges guide discovery by understanding natural language and user context.
For example: A shopper says, "I’m hosting a taco night" or "I need an outfit for a rainy outdoor wedding in Scotland." The agent instantly cross-references inventory, weather forecasts, and style guides to suggest a tailored bundle, creating a faster, more convenient experience that drives engagement.
2. Hyper-Personalization via Real-Time Context
A full 81% of shoppers prefer brands that personalize their experience. AI agents take this to the next level by combining CRM data with real-time context signals like customer sentiment, cart status, and even local events.
For example: An e-commerce AI agent can detect that a shopper has stalled on the checkout page for a high-value item. It can proactively offer a time-sensitive coupon for free shipping or a discount before they bounce, helping to close the sale in the moment.
3. Size, Fit, and Compatibility Guardian
The tactile gap continues to drive bracket shopping and inflated return rates in e-commerce. When shoppers cannot confidently assess fit or appearance, uncertainty becomes a cost center.
Alhena AI addresses this with vertical AI agents such as Fit Analyzer and Virtual Try-On. Shoppers can upload a full-body image to visualize how a garment fits on their own frame, see realistic previews, and receive color palette recommendations aligned with their skin tone.
Combined with past purchase data, these agents deliver precise fit guidance and significantly reduce returns by replacing guesswork with visual and data-driven certainty.
Vertical AI Agents Demo
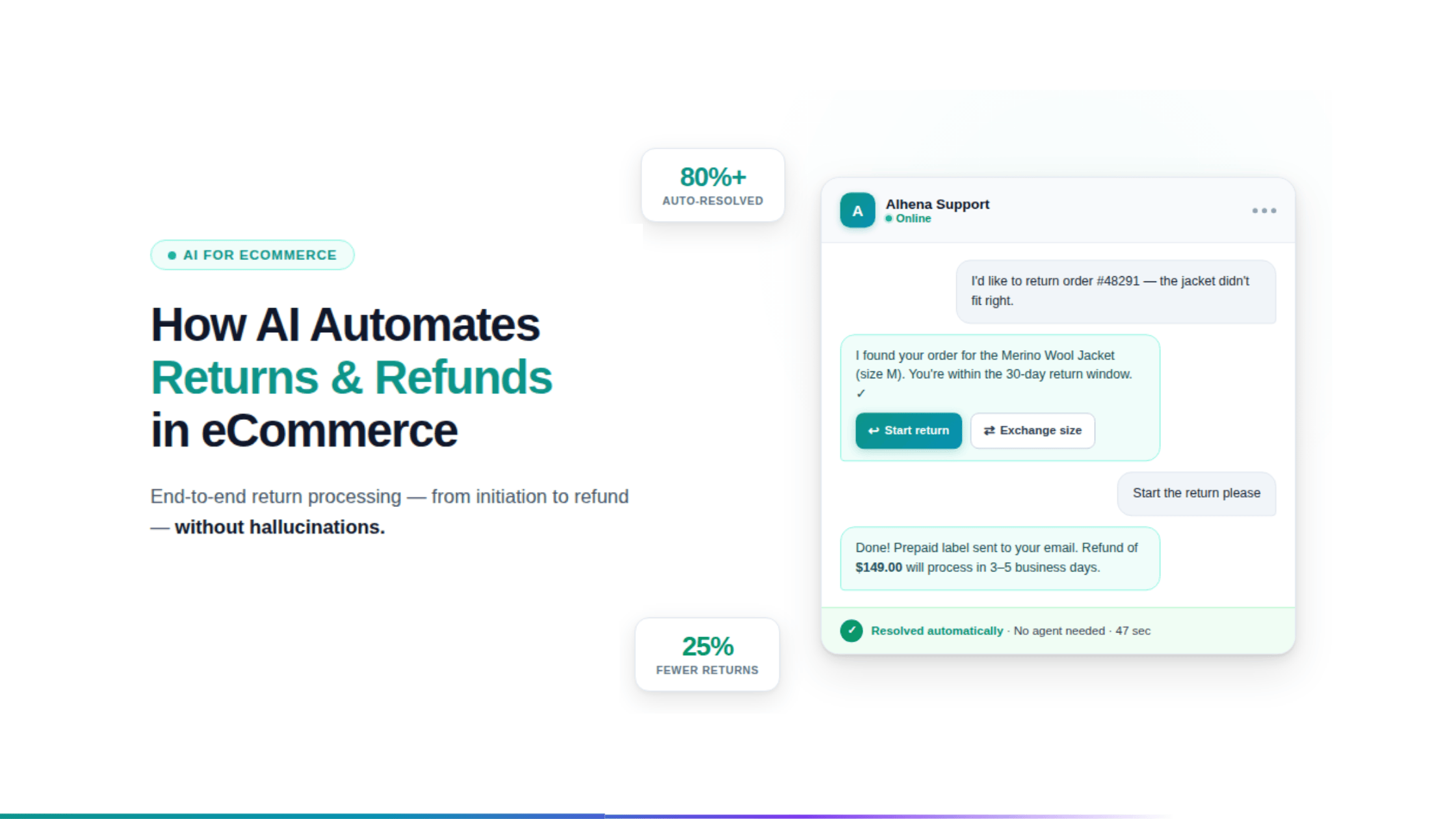
4. Hallucination-Free L1 Support Automation
The greatest fear of early AI was the "hallucination" of policies. In 2026, Alhena AI’s architecture ensures agents are grounded in a brand’s specific "source of truth."
For example: The agent handles 90% of "Where is my order?" (WISMO) and refund status queries by pulling live data from shipping carriers and ERPs. It provides 100% accurate, policy-aligned answers without human intervention, dramatically reducing ticket volume.
5. Enhanced CX with Continuous Conversations
Success in 2026 depends on earning loyalty from selective shoppers. AI agents eliminate friction by remembering past interactions, allowing brands to bring a new level of continuity to their CX.
For example: An e-commerce agent can greet a returning customer and resume a conversation exactly where it left off, regardless of whether it started on WhatsApp or email. It can pre-populate the chat with relevant info, such as alternate sizes for a recently viewed item, ensuring the customer never has to repeat themselves.
6. Proactive Post-Purchase Retention
The relationship shouldn't end at checkout. AI agents manage the "silent period" between purchase and delivery to ensure long-term loyalty.
For example: An agent monitors delivery tracking and, two hours after a "Delivered" status appears, sends a personalized video or guide on how to set up the product. This ensures the customer has a "success moment" immediately, increasing Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
Which e-commerce workflows are best suited for AI agent automation?
The best ecommerce workflows for AI agent automation include order tracking, returns and refunds, inventory queries, cart assistance, size and fit guidance, and post-purchase support that requires contextual understanding.
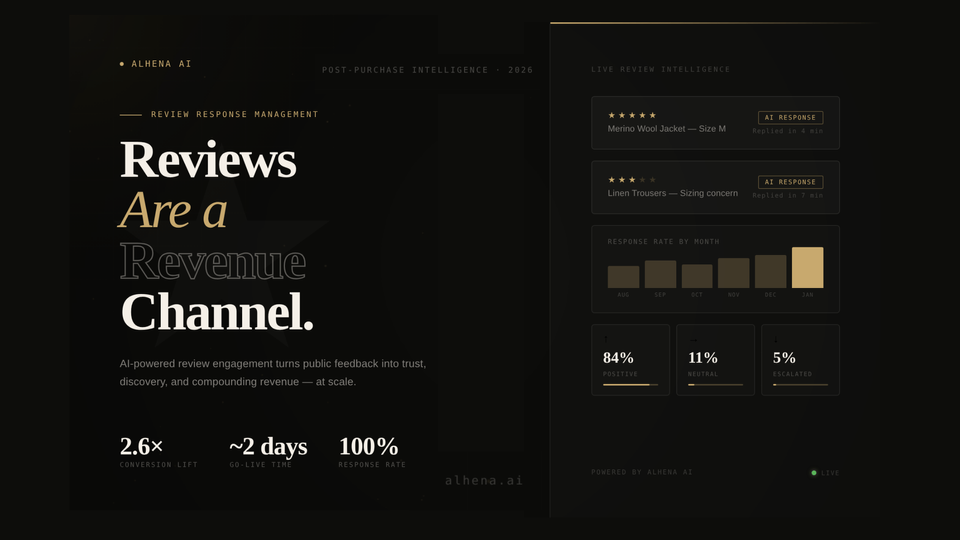
7. Real-Time Merchandising Intelligence
AI agents serve as the "eyes and ears" on the digital floor, feeding insights back to the business to optimize operations.
For example: An agent identifies a specific friction point: "12% of shoppers today asked if the summer collection comes in petite sizes." This insight is automatically pushed to the merchandising team’s dashboard, allowing for extreme agility in inventory and product development.
What role do AI agents play in e-commerce cart optimization?
AI agents assist shoppers in the cart by answering last-minute questions, resolving shipping or inventory concerns, and recommending relevant add-ons. This reduces hesitation and improves checkout completion rates.
8. Agent-to-Agent "Personal AI" Negotiation
As consumers adopt their own personal AI assistants, brand agents must be ready to communicate "machine-to-machine". This is the ultimate evolution of frictionless commerce.
For example: A customer’s personal AI pings a brand’s AI agent to negotiate the best price for a specific SKU or to find a delivery slot that fits the user's calendar, completing the transaction autonomously.
9. Intelligent "Human-in-the-Loop" Routing
An agent knows its limits. By identifying complex emotional nuances, agents ensure that human talent is used where it matters most.
For example: If an agent detects high frustration or a complex sentiment, it seamlessly hands off to a human agent. It provides a concise summary of the interaction history, ensuring a smooth transition that accelerates issue resolution and boosts customer satisfaction.
Smooth AI to Live Agents
Why Most AI Implementations Fail (And How Alhena AI is Different)
The market has realized that generic LLM wrappers are a liability. They hallucinate, they are expensive, and they lack an e-commerce context. Alhena AI powers these use cases through a shopping-first architecture:
- Deterministic: Agents follow your brand’s logic with zero hallucination.
- Integrated: They connect directly to Shopify, SFCC, Gorgias, and Zendesk.
- Outcome-Oriented: We measure success by revenue lift, not just deflection.
Why AI Agents Are the Strategic Frontier for Ecommerce
E-commerce leaders are no longer debating if AI will reshape digital commerce. The conversation has shifted to how AI agents can be operationalized to deliver measurable business outcomes.
Conclusion
In the agentic era, the competitive advantage belongs to brands that offer the least friction. The question for ecommerce leaders is no longer whether to use AI agents, it’s whether your competitors’ agents are already outperforming your human-only workflows.
Schedule a demo to see Alhena in action.
FAQ
How do e-commerce AI agents work behind the scenes?
Ecommerce AI agents work by combining large language models with structured commerce data such as inventory, orders, cart status, and policies. They interpret intent, retrieve verified information, and autonomously complete workflows across customer service and shopping journeys.
Why are e-commerce brands moving from chatbots to AI agents?
Brands are moving from chatbots to AI agents because chatbots answer questions, while AI agents automate decisions and actions. AI agents reduce operational load, improve customer experience, and directly impact revenue by guiding shoppers through the buying process.
What problems do e-commerce AI agents solve that automation tools cannot?
Ecommerce AI agents solve intent-driven problems such as product discovery, compatibility questions, and multi-step customer service workflows. Traditional automation tools rely on static rules, while AI agents adapt dynamically to each shopper’s context.
How do AI agents impact e-commerce customer service costs?
AI agents reduce customer service costs by automating repetitive L1 interactions, lowering ticket volume, and minimizing human involvement in routine workflows while maintaining service quality.